28 December 2025, Volume 35 Issue 1
-
Select all|
-
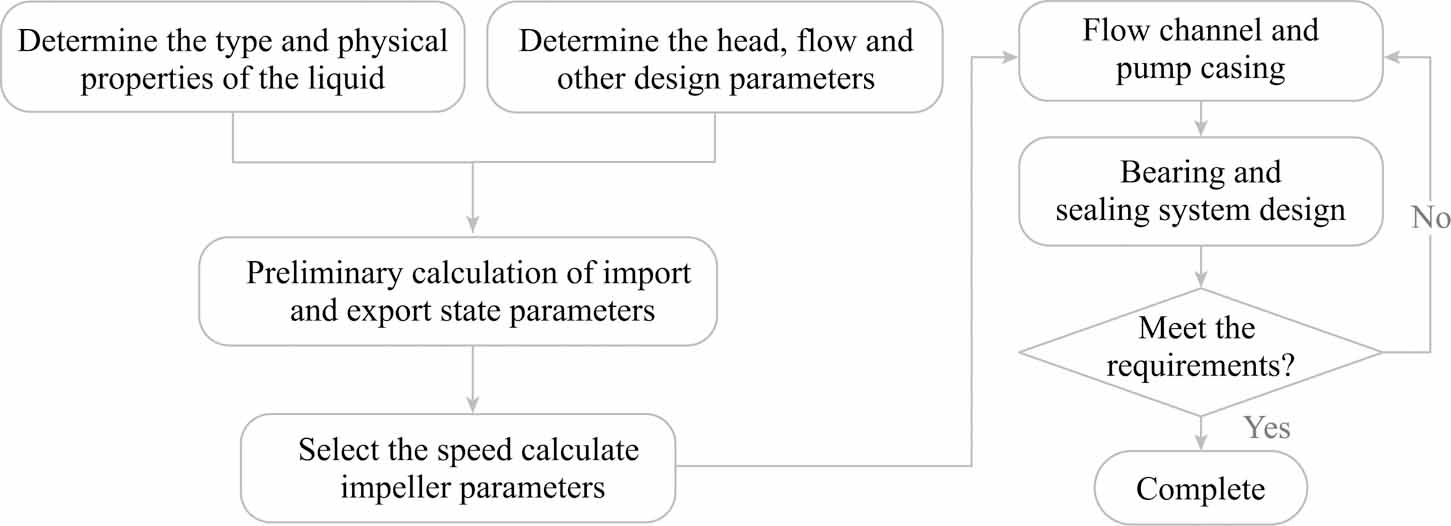
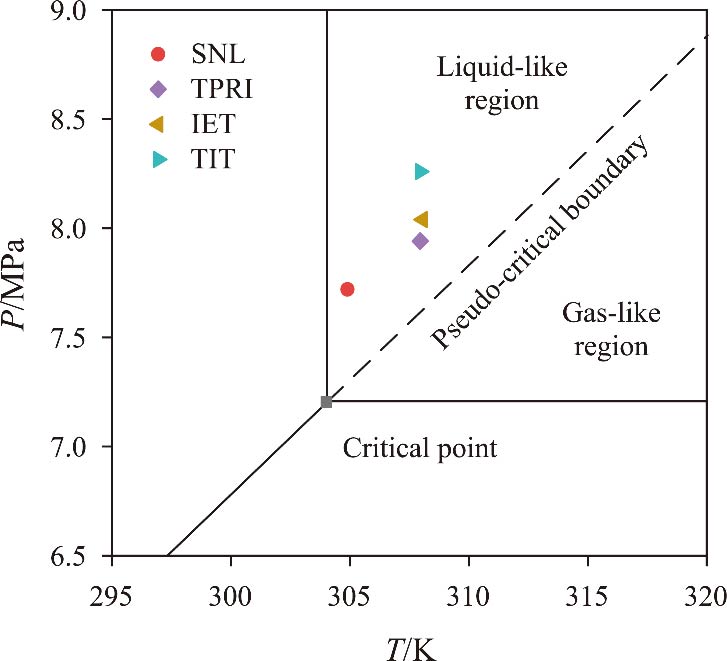
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2218-yAs an emerging energy conversion technology, the supercritical carbon dioxide (SCO2) Brayton cycle offers advantages, including a compact structure and high efficiency. As a core component of the power cycle, the performance of pressurization equipment significantly impacts the cycle’s thermal efficiency. SCO2, as a working fluid in a state between gas and liquid phases, allows for the selection of pumps for liquid pressurization or compressors for gas pressurization. In the context of SCO2 power cycles, current domestic and international research on SCO2 pressurization primarily focuses on centrifugal compressors, with limited attention paid to the feasibility and performance of centrifugal pumps. This study compares the structural design principles of centrifugal pumps and centrifugal compressors, analyzes the challenges posed by the supercritical state of the working fluid to the selection and design of pressurization equipment, and identifies key difficulties in the design and numerical simulation of SCO2 centrifugal pumps. Additionally, the feasibility of centrifugal pumps as pressurization equipment for SCO2 power cycles is evaluated, along with the design and operational considerations that must be addressed. Future investigations into three-dimensional flow phenomena will serve as a critical reference for the design of supercritical CO2 centrifugal pumps.
-
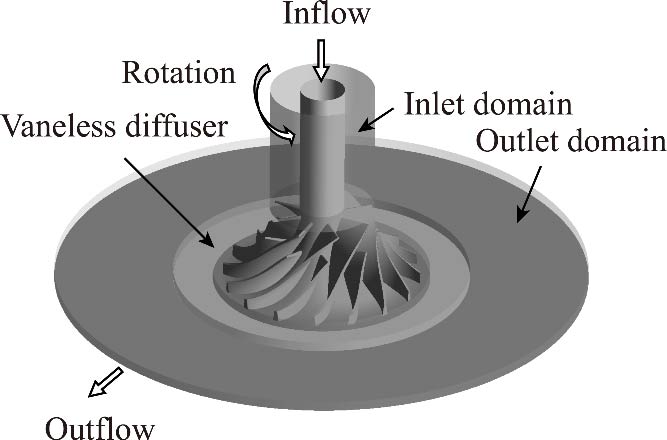
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 15-34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-026-2215-9The high-density nature of supercritical carbon dioxide (S-CO2) allows for compact centrifugal compressor designs, where small absolute tip clearances result in relatively large normalized clearance ratios. This increases leakage flow at the impeller outlet, altering the velocity distribution, especially compared to air compressors. Steady-state simulations were conducted to investigate different relative tip clearances (CR=0%, 3.33%, 6.66%, and 10%). The results show that due to size effects, the types and distributions of secondary flows and vortices within the impeller vary significantly with tip clearance, affecting the jet-wake distribution at the impeller exit and the stall region in the diffuser. When the relative tip clearance exceeds a certain threshold, some secondary flow becomes trapped in the clearance, moving towards the impeller outlet and forming a low flow velocity region on the shroud side. Additionally, when the relative clearance is small, the wake region is primarily affected by channel and separation vortices. As the relative tip clearance increases, the secondary flow in the channel weakens, while the leakage flow intensifies, causing the leakage vortex to extend and dominate at higher blade heights, at the same time, the separation vortex to be formed near the suction side at mid to high positions. Consequently, the core region of the wake at the impeller outlet shifts from the hub side to the casing side, and the reverse flow region in the diffuser shifts from below 20% span (near the hub) to above 80% span (near the shroud).
-
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 35-49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2203-5The compression power consumption of the working fluids in the near-critical region is low. However, there is currently no research on the common characteristics of near-critical region compression for different types of working fluids. This paper takes H2O, CO2, and R134a as research subjects, and based on the common characteristics of the physical properties of working fluids in the near-critical region, a 1D common design method and performance prediction model for near-critical compressors are proposed. Meanwhile, 3D models of centrifugal compressors are established based on the 1D design results. The 3D numerical simulations results show that there is about a 4% error between the numerical simulation results and the 1D performance prediction. Therefore, a slip factor model and a flow correction coefficient are introduced to account for the impact of rotating speed and mass flow rate changes on the loss models. At the same time, the friction loss coefficient and through-flow loss coefficient are corrected based on the viscosity of different working fluids. After optimization, the error under off-design conditions between the numerical simulation results and the 1D performance prediction results is maintained within 1.2%, demonstrating the advantage of the new model in predicting the near-critical compression performance of different working fluids.
-
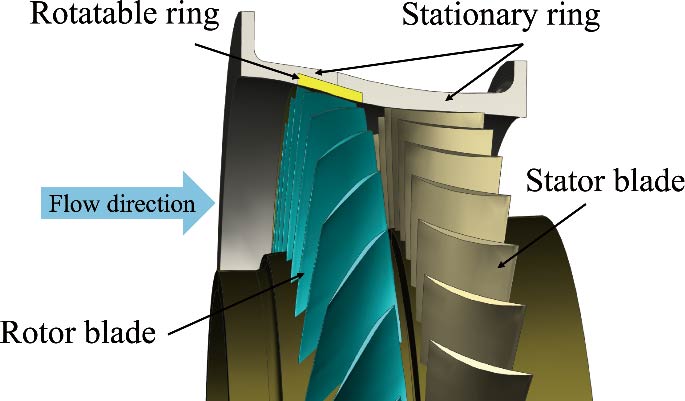
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 50-61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2213-3Controllable speed casing (CSC) represents an innovative development in casing treatment technology, wherein the traditional stationary casing is reconfigured into two components: a rotatable ring and a stationary ring. Initial position (IP) of the rotatable ring is a critical parameter affecting the operational effectiveness of CSC. This study investigates the influence of varying IP of the rotatable ring on the aerodynamic performance and flow stability of a high-load compressor stage, with terminal position (TP) fixed at the rotor tip trailing edge. The results reveal that positioning the rotatable ring near the rotor tip trailing edge leads to moderate improvements in stability by controlling the secondary flow at the trailing edge. However, when IP coincides with the region where the tip leakage vortex and induced vortex breakdown, CSC disrupts the upstream flow, increasing the blockage of low-energy fluid, thereby precipitating an early stall in the compressor. Conversely, positioning IP at the rotor leading edge enables CSC to effectively manage tip leakage flow, facilitating the deflection of the tip leakage vortex away from the adjacent blade pressure surface. This adjustment mitigates the blocking effect within the blade tip passage, thereby significantly enhancing the compressor’s flow stability. Under these optimal conditions, CSC achieves a substantial 45.11% improvement in stable operating margin of the compressor.
-
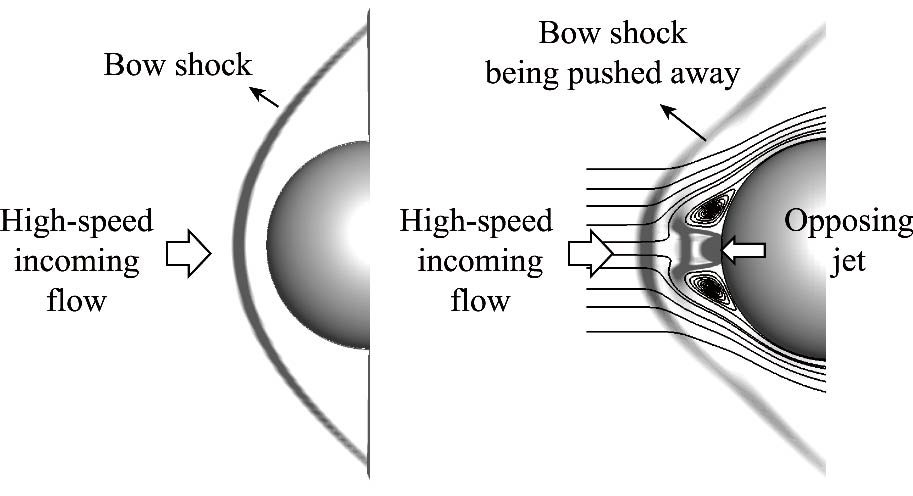
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 62-81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-026-2224-8The opposing jet technique has the potential to provide superior aerothermal protection for long-term high-speed flight in the atmosphere. However, the single-hole opposing jet has certain limitations, including a high requirement for jet injection pressure and inadequate maneuverability. To overcome this, a novel multi-hole opposing jet concept has been proposed, comprising a primary hole located at the stagnation point and multiple secondary holes located downstream. The findings indicated that a secondary hole positioned inside the primary jet recirculation vortex can inhibit primary jet flow reattachment and mitigate peak reattachment heat flux. A smaller secondary hole could impede the lift-off effect of the downstream vortex, facilitating efficient heat reduction at various jet injection pressures. The side-by-side and staggered multi-hole opposing jet configurations were established, which demonstrated an efficacy in reducing the peak heat flux by 11.7% statistically compared to a single-hole injection at the same mass flow rate. When an incoming angle of attack was presented, the multi-hole arrangement exhibited a further peak heat flux reduction of 12.2% by statistical analysis. The results underscore the effectiveness of multi-hole configurations with low-pressure injection in reducing heat and enhancing maneuverability, while demonstrating stronger engineering applicability than traditional combined thermal protection systems without structural compromises or flow instability risks.
-
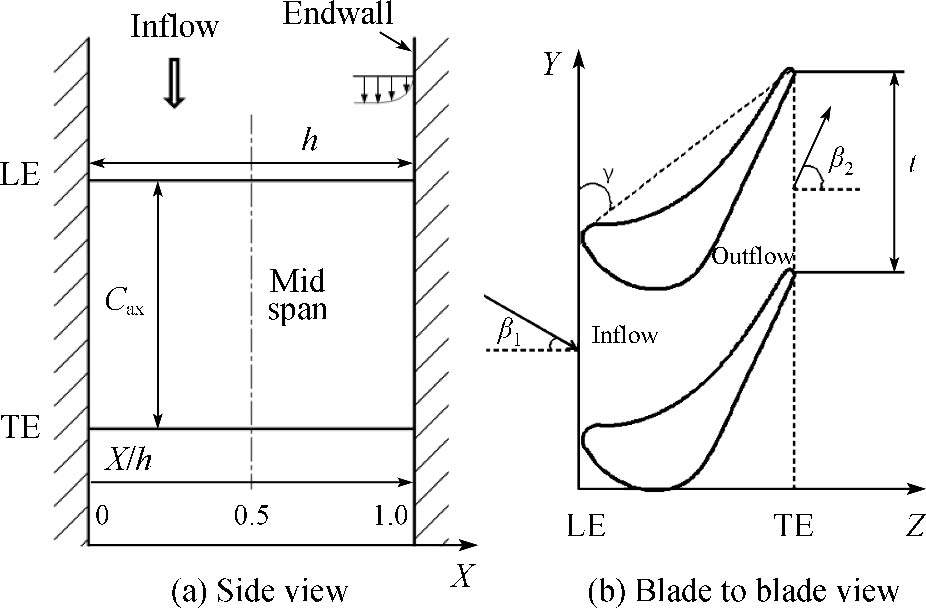
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 82-96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2193-3This paper established a non-axisymmetric endwall optimization profiling platform based on genetic algorithm and designed a non-axisymmetric endwall for a transonic turbine based on the platform. The results show that compared with the original turbine cascade, the total pressure loss of turbine cascade after endwall profiling is reduced by 19.2%. Analyzing the three-dimensional flow field of the turbine cascade before and after endwall profiling, the transverse pressure gradient decreases in the upstream of the turbine cascade but increases in the downstream of the turbine cascade due to the endwall profiling. The corner vortex has a large deflection at the cascade outlet and fuses with passage vortex in the adjacent passage. This also makes the loss near the endwall region at downstream of outlet increase. In the supersonic zone, the air flows through the convex surface close to the suction surface to form a series of isentropic compression waves. The isentropic compression waves interact with the shock wave in the passage, reducing the intensity of the shock waves in the passage in the near endwall region and reducing the shock loss of the turbine cascade, which is the main reason for the reduction of the total pressure loss after the turbine cascade endwall profiling. The non-axisymmetric endwall has good adaptability at different incidence and different outlet Mach number. But when the out Mach number is lower than 0.54 or higher than 1.20, the total pressure loss could not be reduced with the non-axisymmetric endwall. When the outlet Mach number is lower than 0.54, flow in the turbine cascade is in subsonic and there is no shock wave in the passage. The transverse pressure gradient of upstream decreases while the transverse pressure gradient of downstream increases, which has little effect on secondary flow near endwall. Therefore, the total pressure loss of the turbine cascade doesn’t change obviously. When the outlet Mach number is higher than 1.20, the shock wave structure in the passage has changed, so the non-axisymmetric endwall can’t reduce the total pressure loss of the turbine cascade.
-
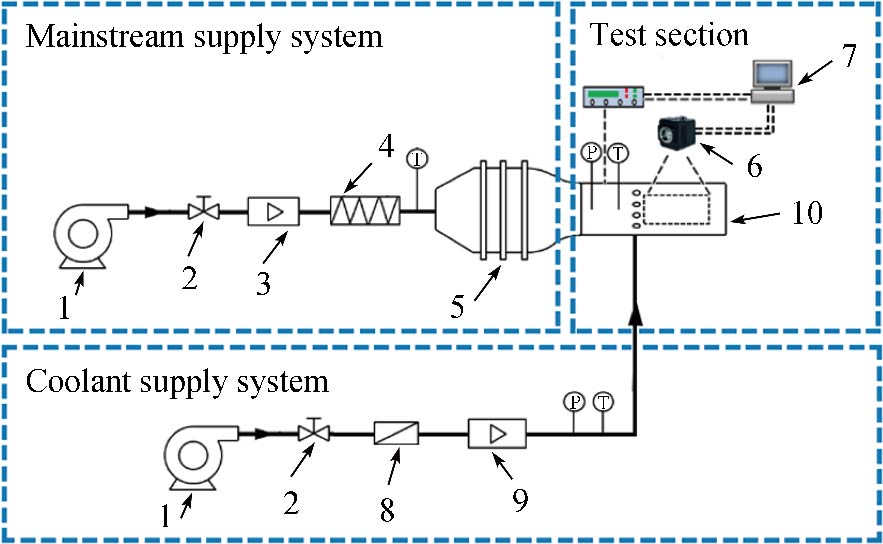
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 97-114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2208-0Film cooling remains a critical technique for protecting turbine blades under high thermal loads, yet developing high-performance film cooling structures while maintaining structural integrity and manufacturability remains a major challenge. Serrated trenched-hole designs offer enhanced coolant coverage and manufacturability advantages over conventional shaped holes, but their performance under various streamwise pressure gradient conditions has not been systematically explored. This study investigates the impacts of mainstream streamwise pressure gradients, including zero, adverse, and favorable, on characteristics of serrated trenched-hole film cooling, with comparisons to conventional cylindrical holes. A combination of experimental measurements and Large Eddy Simulation (LES) is employed to investigate flow dynamics and film cooling performance under various pressure gradients and at blowing ratios of M=0.5 and M=1.5. Experimental results demonstrate that the serrated trench consistently enhances film cooling effectiveness. Under adverse pressure gradients, it mitigates the reduction in film cooling performance and improves both streamwise and spanwise coverage. Particularly at M=1.5, the serrated trench improves near-exit region film cooling effectiveness by roughly 2–3 times compared to cylindrical holes. Under favorable pressure gradient, the serrated trench further optimizes cooling effectiveness by promoting both spanwise continuity and streamwise expansion of the coolant film, with the maximum film cooling effectiveness in the near-exit region reaching approximately 0.9. Favorable streamwise pressure gradients enhance the laterally averaged film cooling effectiveness of the serrated trench by 10%–18% compared to the zero-pressure gradient case, especially at M=1.5. While adverse pressure gradients lead to a modest reduction of film cooling effectiveness, with decreases of up to 10% in the near-exit region at M=0.5 and 10%–15% in the far-field at M=1.5. LES results at M=1.5 reveal that film cooling enhancement under favorable pressure gradients is closely associated with the formation of Anti-CVP (Anti-Counter-rotating Vortex Pair) and inter-hole vortices, which facilitate lateral coolant transport and improve spanwise coverage. Conversely, adverse pressure gradients induce jet lift-off, intensifying mainstream-coolant mixing, leading to diminished cooling effectiveness. Turbulence kinetic energy (TKE) analysis further supports these findings. The novelty of this work lies in its quantitative assessment of streamwise pressure gradient effects on trenched-hole film cooling, which is scarcely addressed in prior research, and in its integrated use of experimental and LES approaches to elucidate both performance trends and underlying flow mechanisms.
-
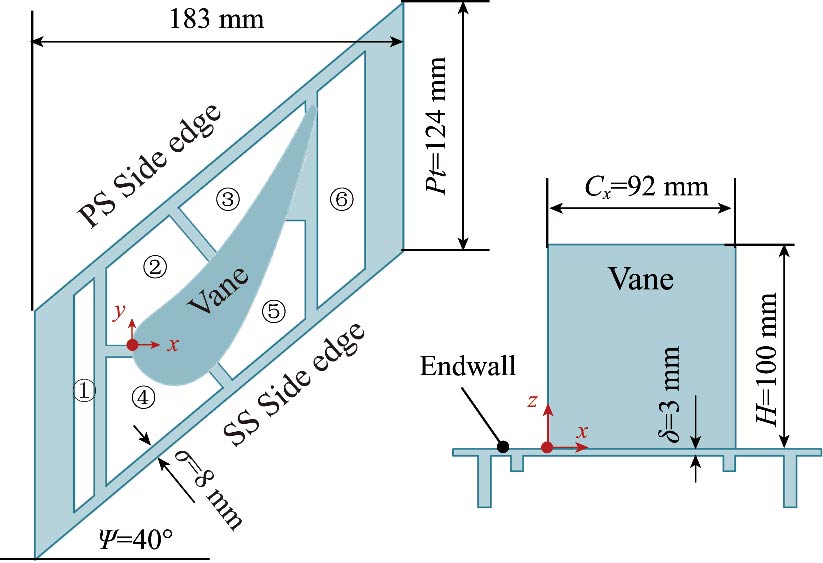
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 115-131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2210-6Endwall film-cooling effectiveness experiments were conducted on a turbine guide vane using pressure sensitive paint measurement technique. Four film hole geometries, i.e., a fan-shaped hole, a horizontal slot hole, and two vertical slot holes with different expansion angles, were tested under a film hole layout that considered the actual multi-chamber construction. A continuous slot was set upstream of the endwall film holes to examine the influence of the upstream cooling. The experiments were performed at a mainstream Reynolds number of 620 000, a mainstream turbulence intensity of 3.7%, and a coolant-to-mainstream density ratio of 1.5. The results showed that the vertical slot holes perform better in the various chamber zones on the endwall than other hole geometries, in particular the zone with highly accelerated mainstream and the zone with large orientation angle. The vertical slot hole with a large exit expansion angle always yields the highest effectiveness on the endwall. The upstream slot cooling remarkably improves the endwall effectiveness and the influences are almost consistent for various hole geometries. Compared with the baseline fan-shaped hole, from blowing ratios of 1.0 to 2.5, the increase in the area-averaged effectiveness by large expansion angle vertical slot hole reaches 10.7%–39.1% without upstream slot cooling, while with upstream slot cooling, the increase decreases to 4.9%–23.1%. The discharge coefficient of various hole geometries on the endwall has almost no difference at small blowing ratios, and the difference at medium and high blowing ratios is also not great.
-
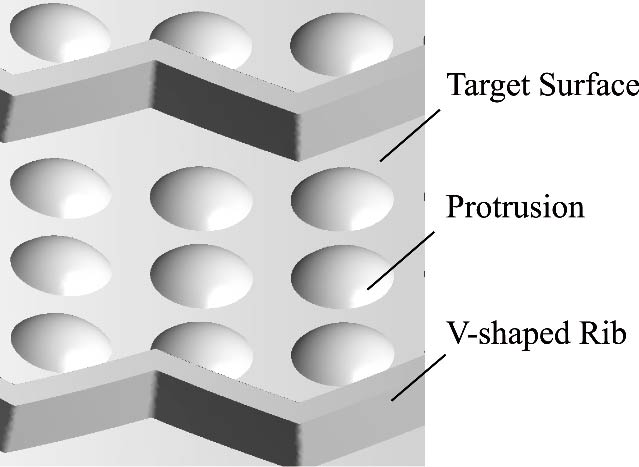
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 132-150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2199-xIn this study, the conjugate heat transfer method is employed to numerically investigate the thermal performance of the inner wall surface with different turbulators (i.e., ribs or protrusions) in a turbine guided vane. The effects of turbulators on flow and heat transfer are analyzed in detail, including their influence on pressure and velocity distributions, Nusselt number distributions, and flow fields. Through quantitative analysis, the results show that the introduction of ribs or protrusions dramatically increases the discharge coefficients of jet nozzles (by up to 71.5%) and the heat transfer (by up to 47.3%) between coolant and vane inner wall, while inhibiting the effusion of film holes, especially when ribs are adopted. Furthermore, all turbulators feature blockage effects on the flow of coolant, which can reduce the coolant assumption by up to 2.28%. A comparative analysis of various cooling structures reveals that the vane inner wall incorporating orthogonal ribs and protrusions exhibits the highest overall cooling effectiveness, exceeding that of the vane inner wall without turbulators by 0.0249. These findings provide valuable guidance for the design and optimization of advanced cooling structures in turbine blades.
-
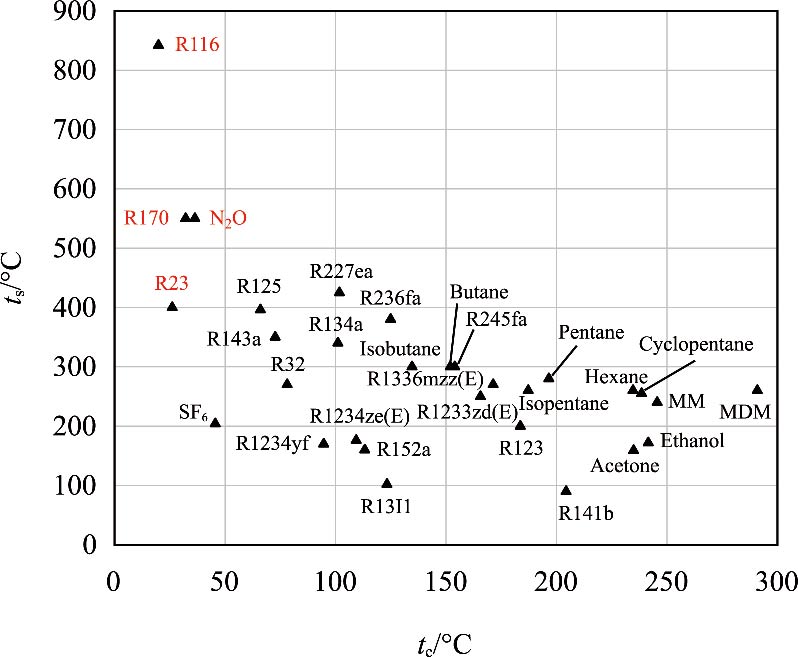
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 151-167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2200-8Middle and low temperature thermal energy widely exists in the natural world and many industrial fields. Unlike fossil fuel power generation systems, the significant feature of middle and low temperature power generation systems is the temperature constraint of the heat source. Exploring the potential of the cycle within a limited temperature range is key to improve energy utilization efficiency. This study proposes the conception of supercritical organic fluid Brayton cycles (SOFBC) and evaluates the feasibility and application potential. R116, R23, R170 and N2O are selected as the working fluids for cycle analysis based on their thermal properties. Then, thermodynamic models of the supercritical gas Brayton cycle based on simple regeneration and organic Rankine cycles (ORCs) have been established. According to the calculation results, the performances of regenerative Brayton cycles (RBCs) using four working fluids are better than that of CO2. The maximum thermal efficiencies of R116, R23, and R170 are 41.9%, 20.2%, and 15.3% higher than that of CO2 at the highest temperature of 150°C. Even at 300°C, the corresponding values of three organic fluids are 25.6%, 13.7%, and 13.7% higher than that of CO2. By analyzing the variations in isobaric specific heat capacity (cp) of different working fluids, it is found that the cp difference between the high and low pressure sides in the regenerator of CO2 is significantly higher than that of organic working fluids. Additionally, the performance of RBCs using R116 is better than the sub-ORC using R123 and the trans-RORC using R236fa at the same temperature range. The results can demonstrate that the SOFBC is superior in middle and low temperature power generation compared with the sCO2 Brayton cycle and ORCs. This study provides preliminary and rough evidence of the feasibility and potential for SOFBCs.
-
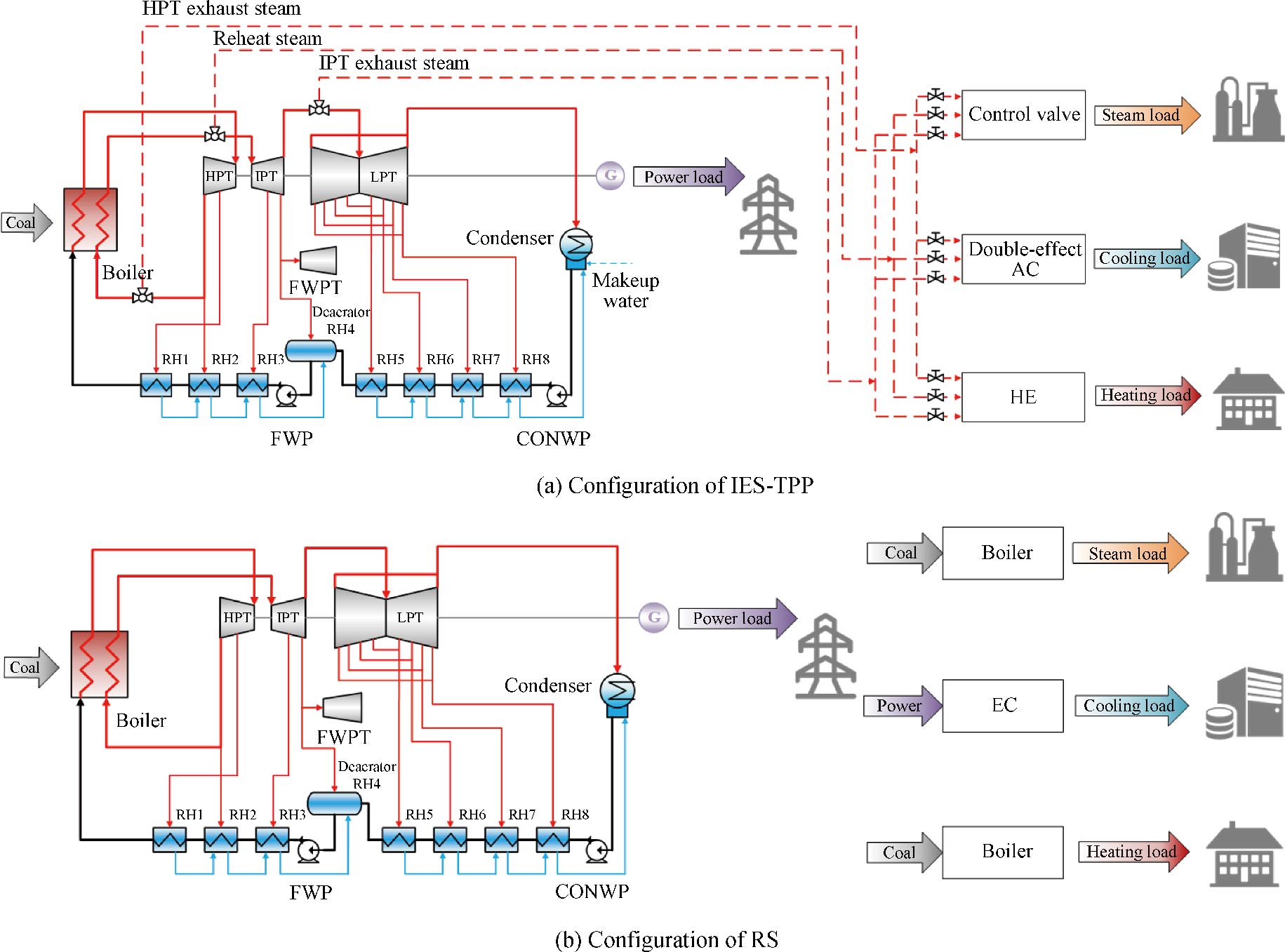
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 168-187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2168-4With the integration of renewable energy sources into energy supply systems, coal-fired thermal power plants require a feasible and effective approach for renovation. This paper combines the technology of steam extraction and the idea of integrated energy system to establish an integrated energy system based on coal-fired thermal power plant. It supplies steam, cooling, heating and power for users by employing unit modifications. And a reference system is set up for comparison. Detailed models for system calculations, thermodynamic performance, and economic indexes are developed. Energy, exergy and economic performances are analyzed on the proposed system. The results show that when the steam, cooling, heating and power loads are 100 t/h, 20 MW, 80 MW and 225 MW respectively, the primary energy utilization rate, total exergy efficiency and dynamic payback period of the proposed system are 61.51%, 36.13% and 1.75 years respectively. Compare to the reference system, the proposed system offers significant advantages in both thermodynamics and economics. Furthermore, a tri-objective optimization algorithm based on the NSGA-II, combined with the TOPSIS, has been developed to optimize the integrated energy renovation of coal-fired thermal power plants; additionally, the optimal supply of energy products is obtained. The optimization method can provide support and reference for the renovation of coal-fired thermal power plants.
-
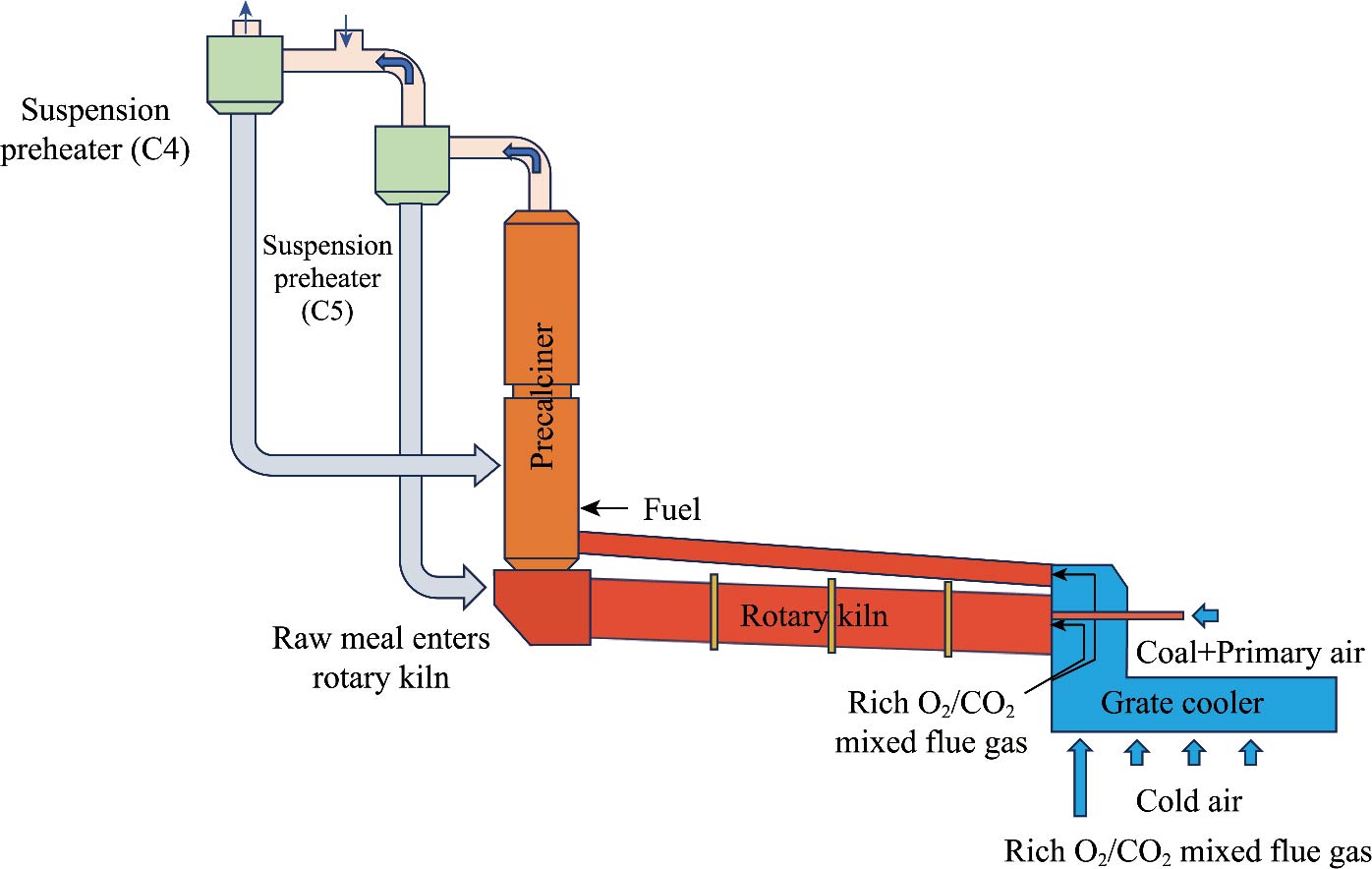
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 188-202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2204-4The cement sector significantly contributes to industrial CO2 emissions, and reducing the carbon emissions of the cement industry has become an urgent problem. Oxy-fuel combustion stands out as the greatest prospective technology in the carbon capture and storage field, with immense potential for achieving carbon reduction objectives. This study employs computational fluid dynamics (CFD) methods to investigate the characteristics of pulverized coal combustion and raw meal decomposition in a cement precalciner. Considering the influence of varying kinetic parameters of CaCO3 on a precalciner, the flow and temperature field distributions, species distributions, raw meal decomposition rate, and NOx generation under 21% O2/79% N2 and 21% O2/79% CO2 atmospheres were analyzed in detail. Results show that changing the combustion atmosphere from 21% O2/79% N2 to 21% O2/79% CO2 has no obvious effect on the flow field. However, the maximum temperature decreases; the NOx emissions are reduced by 19%, and the high concentration of CO2 in the flue gas simplifies the carbon capture process, helping to reduce energy consumption in the decarbonization of the cement industry. In addition, high CO2 partial pressure reduced the decomposition rate of raw meal from 96.6% to 82.3%, and increased the outlet temperature by 118 K. Therefore, the pollutant emissions and carbon capture costs in the cement industry can be effectively reduced under the O2/CO2 atmosphere.
-
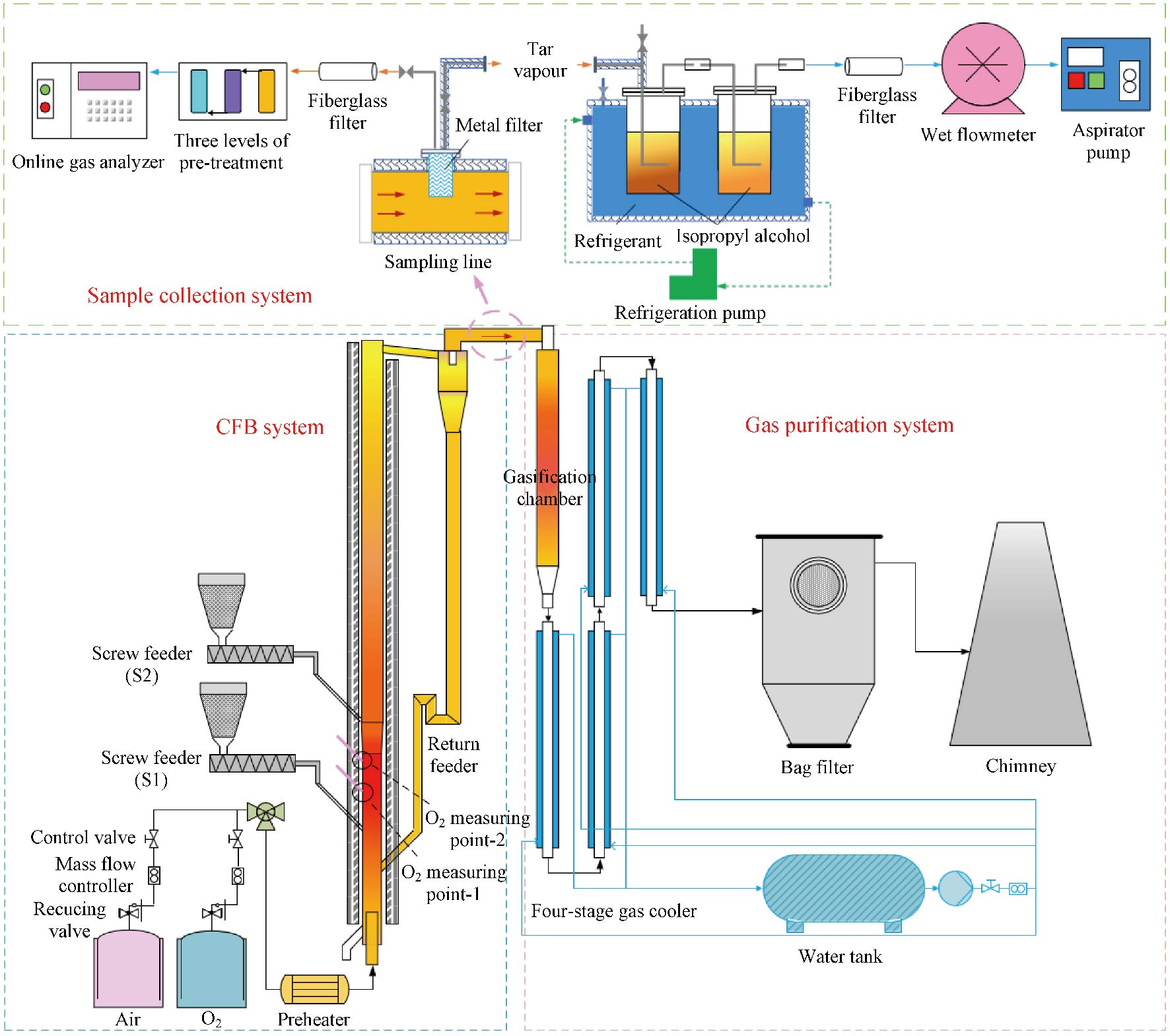
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 203-214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2216-0The pyrolysis behavior exhibited during the coal partial gasification of circulating fluidized bed (CFB) indicates its potential to further increase the pyrolysis efficiency for tar production. To verify and reinforce it, the pyrolysis behaviors of this process at various factors including feeding position, oxygen concentration, and oxygen equivalence ratio were systematically investigated in a bench scale CFB. The distribution and physicochemical properties of gas, liquid, and solid products were focused and the evolution of pyrolysis products was thereby revealed. Experimental results show that raising the coal feeding position reduces the direct contact between coal particles and oxygen, creating a local reduction zone in the upper part of the riser, where the temperature drops sharply. This significantly enhances the pyrolysis effect through protecting the pyrolysis gas from oxidation. In this case, the produced tar is rich in monoaromatic hydrocarbons. Within the oxygen volume concentration range of 21%–33%, increasing the oxygen concentration of the gasifying agent shortens the oxygenated zone in the lower riser, further enhancing the pyrolysis effect. Reducing the oxygen equivalence ratio from 0.19 to 0.13 also results in a higher tar yield. In this study, the maximum tar weight yield reaches 4.97%, accounting for 72.81% of the total tar measured by Gray-King analysis. These results confirm the feasibility of tar production via coal partial gasification in a single CFB.
-
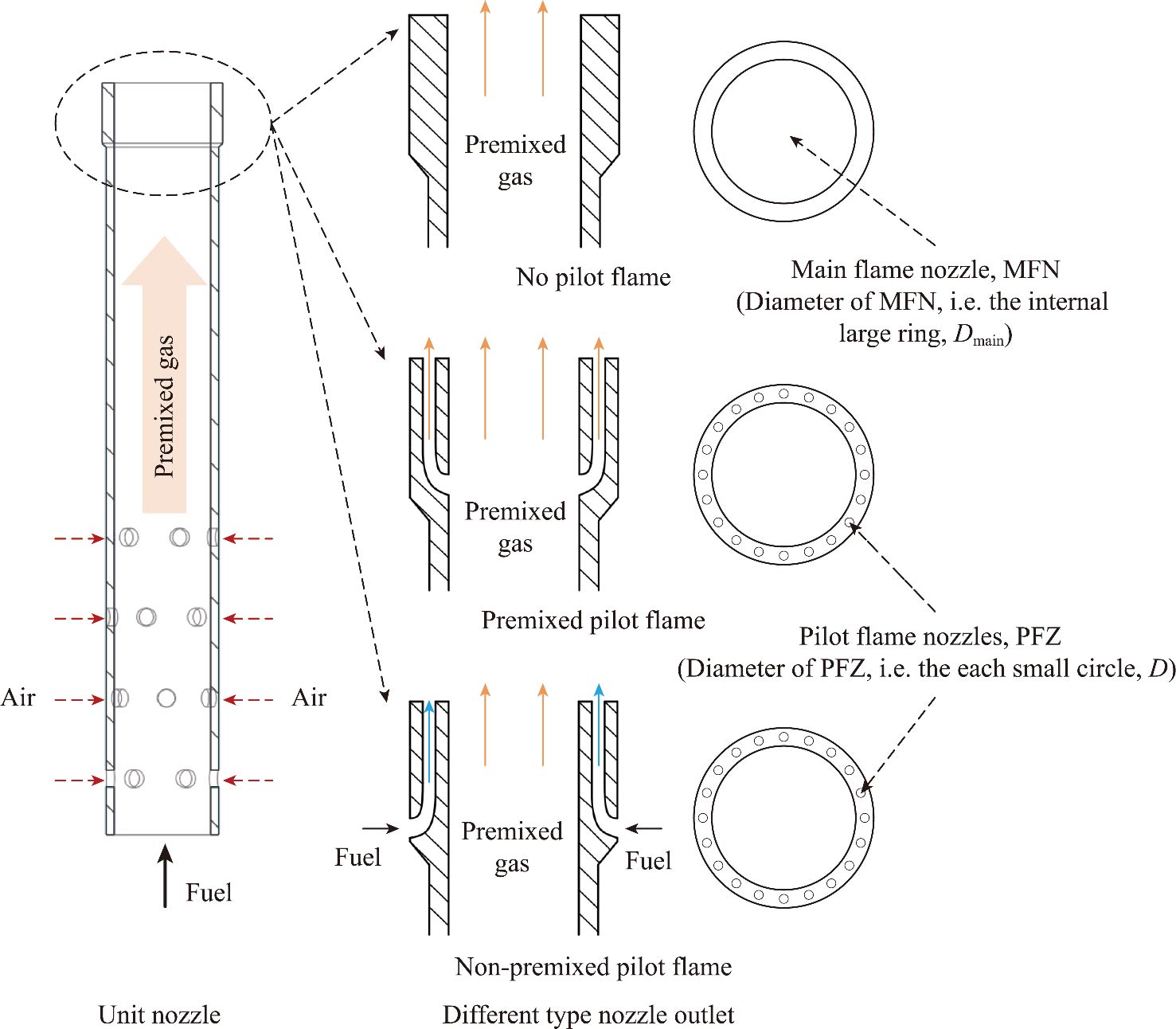
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 215-226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2209-zThe micromix combustor is capable of shortening flame lengths and achieving very low emissions under lean fuel conditions, and mostly uses multi-jet burner. Lacking the traditional swirl flame stabilization mechanism, the limited stability range of multi-jet burner restricts its application in gas turbine combustor, especially for methane fuel. This study presents the development and experimental analysis of a multi-jet burner with pilot flames, using both premixed and non-premixed pilot flames. The design aims to improve lean blowout limit, a critical factor for expanding the operational range and low-load capability. Experiments at atmospheric pressure, along with large eddy simulations, are conducted to illustrate the stabilizing mechanisms and establish pilot flame design criteria. The findings reveal that the stability of the multi-jet burner is primarily depended on the stability of single-nozzle flame. An optimized pilot flame is crucial for the single-nozzle. The premixed pilot flame requires the pilot nozzle diameter to be less than 0.6 mm to provide sufficient heat and radicals to stabilize the main flame, ensuring that the burner stability is improved by 35 K. The non-premixed pilot flames demonstrate a greater potential for stability enhancement, particularly as the pilot fuel ratio increases. In addition, when the pilot fuel ratio is less than 15%, the non-premixed pilot flame has certain NOx emission advantages, achieving a wide range of 252 K for burner stability without causing emission problems. These results provide an innovative perspective on enhancing stability in gas turbine combustors by designing pilot flames on the single-nozzle.
-
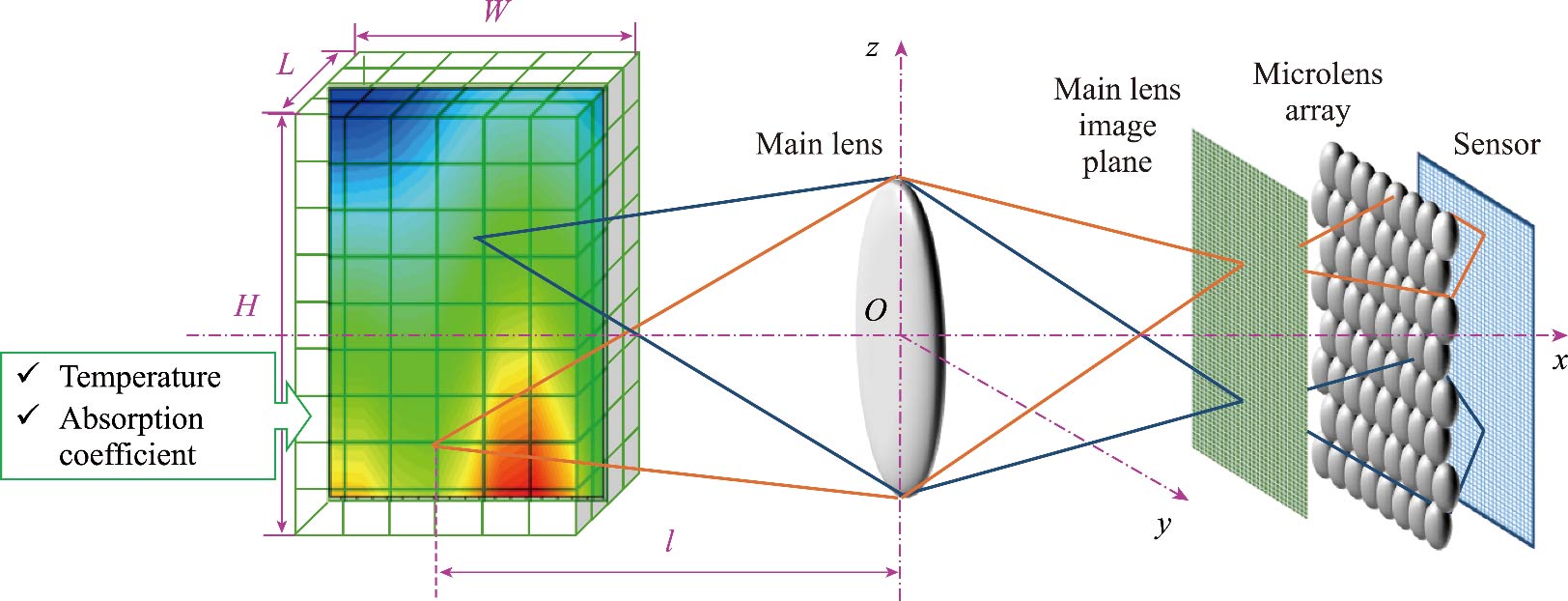
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 227-237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-026-2217-7Asymmetric flames exhibit distinct dynamic characteristics and combustion patterns during combustion, which are crucial for optimizing combustion efficiency and performance. Accurate derivation of three-dimensional temperature and absorption coefficient distributions in asymmetric flames is essential for real-world flame measurement applications. However, retrieving these data presents a significant challenge, as the process requires solving an ill-posed inverse problem. To tackle this issue, we propose a multi-spectral light field imaging model that utilizes the Monte Carlo ray tracing method to capture these distributions. This model enables the reconstruction of both temperature and absorption coefficients using Tikhonov regularization combined with Bayesian optimization method. Our analysis investigates the uncertainties associated with temperature reconstruction, taking into account factors such as uniform and non-uniform absorption coefficient distributions, the reconstruction technique employed, and the signal-to-noise ratio. Notably, our findings suggest that the absorption properties within the flame have a minimal impact due to the flame medium’s optical thickness. Moreover, a comparative assessment between the Tikhonov regularization method and the least-square QR decomposition method reveals that, for comparable accuracy in reconstruction, the Tikhonov method requires a shorter computational time. Ultimately, the uncertainty related to the signal-to-noise ratio emerges as the most influential factor affecting the relative error in the reconstruction of the flame’s absorption coefficient.
-
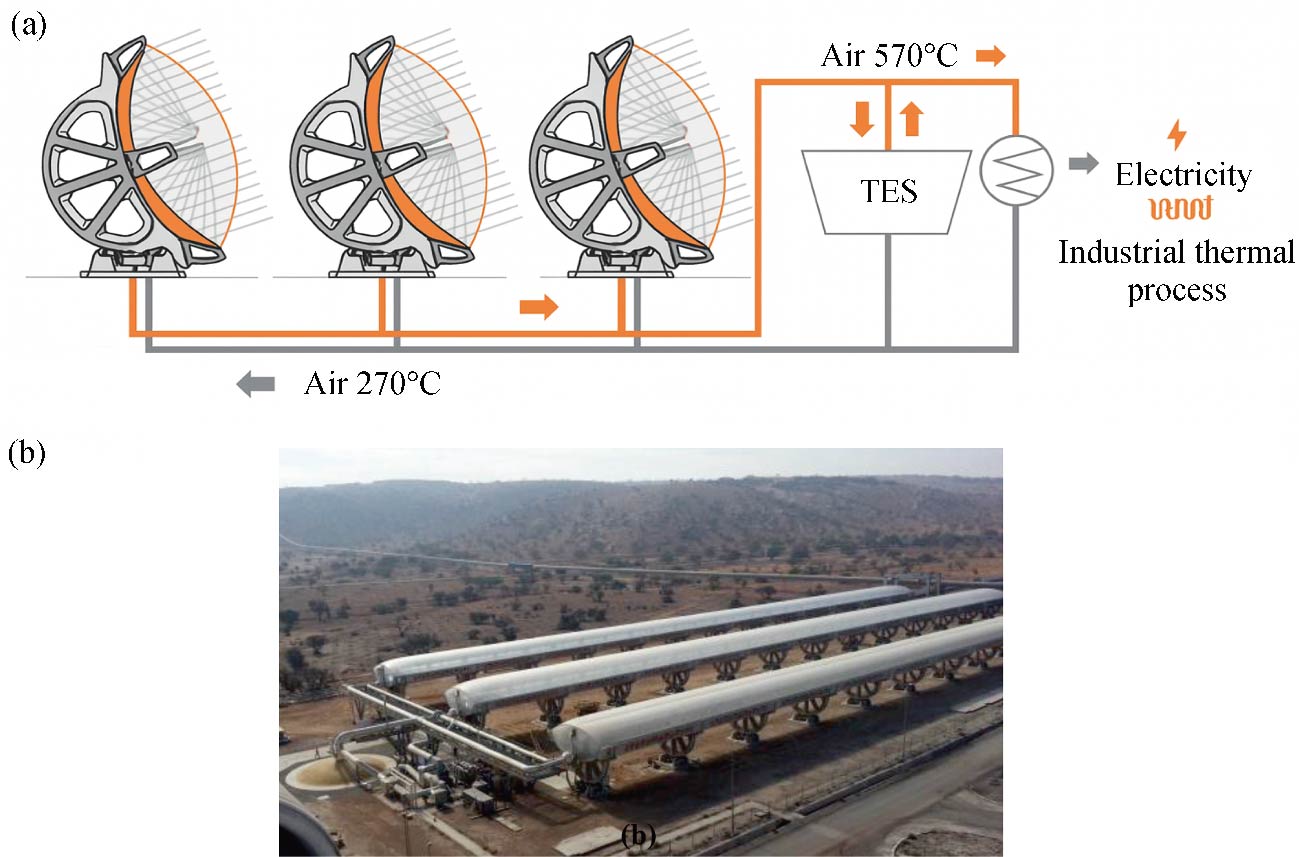
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 238-255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2221-3A rock-bed provides a highly efficient and cost-effective heat storage solution for solar concentrators employing air as the heat-conducting fluid. This pioneering technology was first deployed on an industrial scale at the Ait Baha concentrated solar plant in Morocco, delivering a thermal storage capacity of 100 MWh. This work aims to explore the thermal behavior of large-scale reservoir under real operating conditions and also to explore the impact of pre-charging on system performance. For this purpose, a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) model, rigorously validated through experimental measurements, is employed. Based on the number of Pre-Charging Cycles (PCCs), scenarios with 0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 PCCs were analyzed over 30 days of system operation and compared to the reference case characterized by 0 PCCs. The results demonstrate that starting the system with PCCs significantly improves performance during the early cycles, effectively mitigating initial inefficiencies, enhancing operational efficiency, and reducing the duration of transient behavior during energy input and output phases. The analysis identifies six PCCs as the optimal balance for this system, delivering high efficiency and stabilizing performance with the minimal fluctuations by the 5th operational cycle. Furthermore, a comprehensive guideline is proposed to determine the optimal number of PCCs, ensuring the prevention of system overload and the minimization of energy waste during the pre-charging process.
-
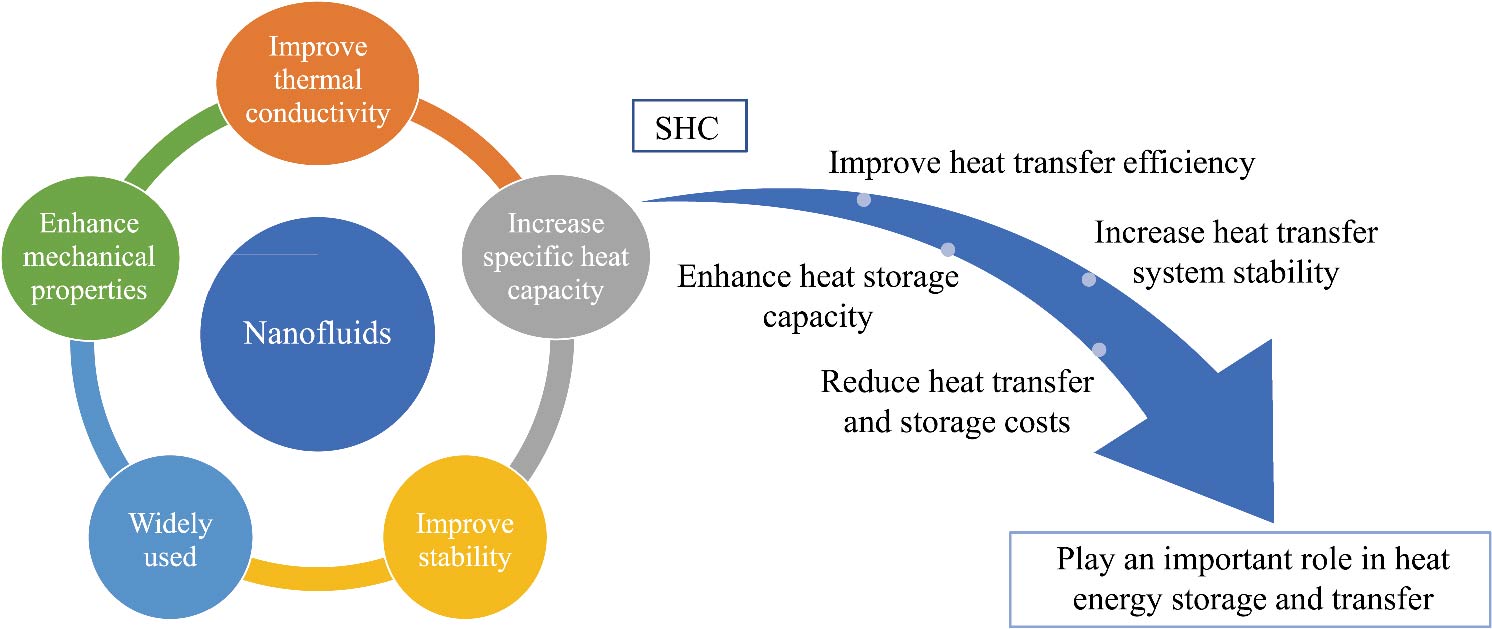
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 256-283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2164-8The distinctive specific heat capacity of nanofluids presents opportunities for enhancing heat transfer efficiency and plays a pivotal role in the design of nanoscale devices. Existing research often overlooks the influence of particle size and nanostructures on the specific heat capacity of nanofluids. Therefore, this paper provides a comprehensive survey that encompasses synthesis techniques, measurement methodologies, predictive models, and influential parameters affecting the specific heat capacity of nanofluids. Empirical investigations have consistently shown that the specific heat capacity of nanofluids typically increases with a reduction in particle size, primarily due to surface and size effects. Furthermore, the specific heat capacity of nanofluids is significantly influenced by temperature and concentration. However, due to the complex interplay of surface effects, temperature gradients, and pressure gradients within nanofluids, the specific heat capacity exhibits nonlinear behavior, thereby complicating the research landscape.
-
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 284-302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-025-2183-5To enhance cooling efficiency by supercritical CO2 in annular structures, this study meticulously explores a rib-splitting strategy. Utilizing Shear Stress Transport (SST) k-ω within ANSYS Fluent, three-dimensional models are developed and simulated, with settings validated against existing experimental data. The investigation focuses on various structural parameters, including the height and position of circular ribs, and the spacing between semicircular ribs. Key findings reveal that a notable enhancement in heat transfer, measured by the comprehensive heat transfer factor, is observed when the rib’s dimensionless height reaches at least 0.25. Closer to the inlet, higher heat transfer performance is achieved, with a dimensionless position of 0.2 exhibiting the best performance across all instances about position effects. The rib-splitting approach has been proven effective in enhancing heat transfer performance, with the comprehensive heat transfer factor increasing progressively with the dimensionless distance and reaching its maximum at a value of 8. The heat transfer enhancement is characterized by an 8.2% increase in the comprehensive heat transfer factor, achieved with a rib’s dimensionless height of 0.5, a dimensionless position of 0.2, and a dimensionless distance of 8. The derived correlations for the Nusselt number (Nu) and friction factor (f) demonstrate the high accuracy of our computational models, as most cases fall within a ±10% deviation range. Crucially, the results advocate for the rib-splitting method’s efficacy in not only enhancing heat dissipation but also in mitigating pressure loss to a significant degree. The insights gained from this study hold considerable promise for thermal management in shafts, potentially elevating both their operational safety and efficiency. The rib-splitting strategy could be a valuable addition to the toolbox of thermal engineers seeking to optimize the performance of their systems.
-
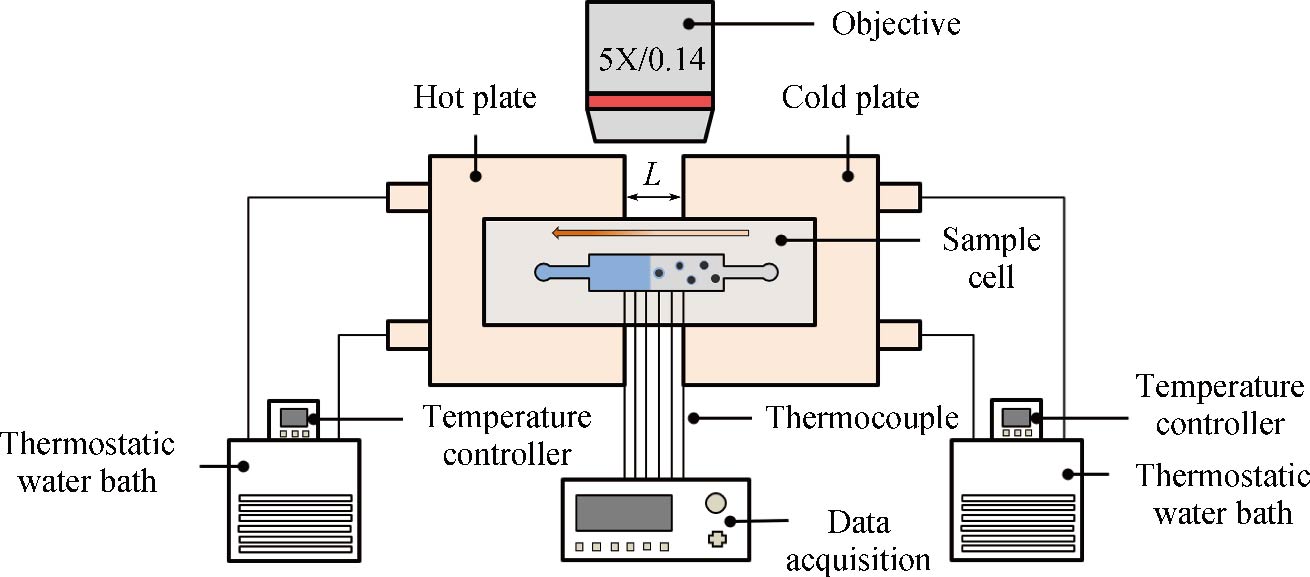
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 303-314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-026-2219-5When particles are embedded in the ice near its bulk melting temperature, a premelted film forms between the particles and ice in a process known as “interfacial premelting”. Under the influence of a temperature gradient, the premelted film varies in thickness, modulating the strength of ice-particle interactions and producing a net pressure that drives the particles to migrate towards higher temperatures in a phenomenon known as “thermal regelation”. The phenomenon of thermal regelation is related to frost heave of soil, cryopreservation of organisms and methods of ice core paleoclimatology. In order to further investigate the principles of thermodynamics and dynamics in thermal regelation, we built a temperature gradient control platform and a single layer visual polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) chip for thermal regelation experiments of individual silica particles. In the experiment, we measured the migration velocity of individual particles at different locations in the ice, and found that the thermal regelation of particles can be divided into high speed and low speed stages. As the particles approach the ice-water interface, the migration velocity increases dramatically. By combining the experimental data with the premelting theory, we found that the observed behavior is phenomenologically consistent with expectations for van der Waals force with radii of 12.5 μm and 10 μm. However, when the particle size was reduced to 7.5 μm, the observed behavior was phenomenologically consistent with expectations for undelayed van der Waals force. In addition, under different temperature gradients and particle sizes, the thickness of the premelted film was maintained in the range of 20 nm–60 nm close to 273.15 K. However, under the same supercooling degree, the thickness of the premelted film increases with the increased of temperature gradient. Among the extracted parameters, the parameter λ, which was related to the van der Waals force, was linearly related to the temperature gradient. These experimental results not only provided important quantitative information for further understanding of thermal regelation but also provided a theoretical basis for optimizing related applications.
-
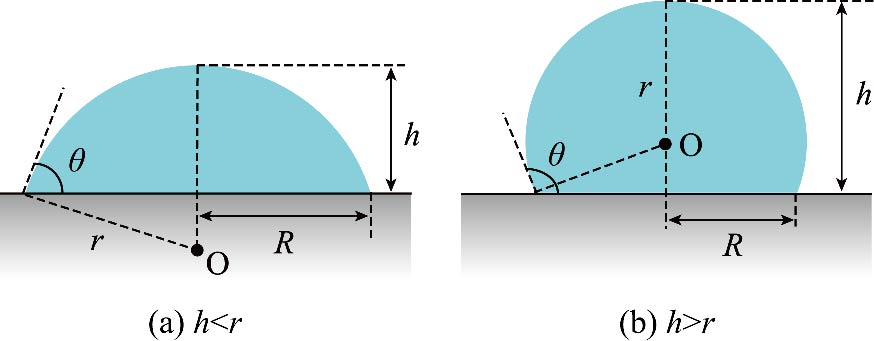
Journal of Thermal Science. 2026, 35(1): 315-328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-026-2220-zLiquid gallium has a super smooth flexible surface. Compared with traditional rigid metal surfaces, the surface roughness of liquid gallium is much smaller. This study investigated the evaporation of hexane nanodroplet and water nanodroplet on heated liquid gallium surfaces through molecular dynamics simulations, and analyzed the influence of interactions between microscopic particles on evaporation process. The findings suggest that during hexane droplet evaporation, the contact angle stays almost constant, whereas the contact radius progressively shrinks, following the constant contact angle (CCA) mode. During water droplet evaporation, the contact radius stays relatively constant, whereas a progressive reduction in the contact angle is observed, which belongs to the constant contact radius (CCR) mode. The difference between these two evaporation modes is ascribed to competition between intermolecular forces near the contact line and intermolecular forces on the liquid surface during the evaporation process. Water exhibits greater surface tension compared to hexane, which suppresses water molecules from escaping across the vapor-liquid interfacial region. The intermolecular forces in the vicinity of the contact line serve to anchor water droplets to the surface. The hydrogen bonds formed between adjacent water molecules further enhance this interaction, leading to the phenomenon of contact line pinning. Compared with water droplets, rapid shrinkage of contact line during hexane droplets evaporation increases fluctuations on flexible liquid gallium surface, thereby accelerating droplet evaporation. The present work offers a reference for applying liquid metal in flexible electronics.