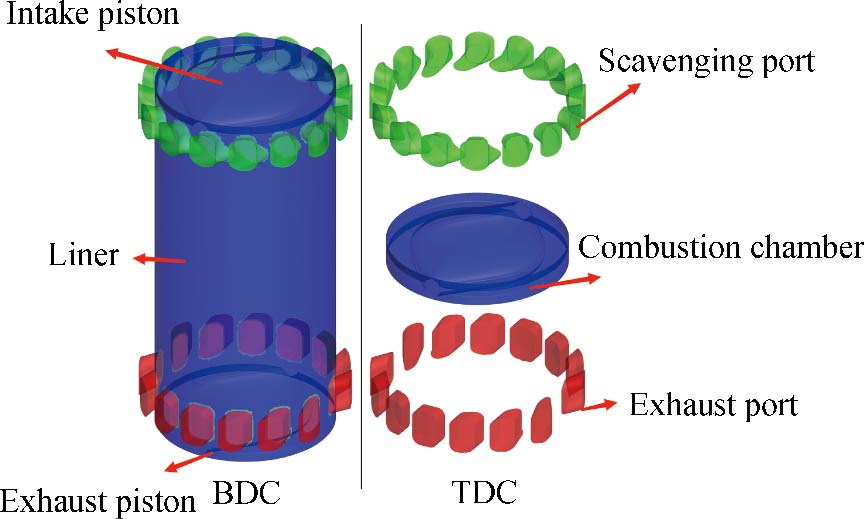
[1]
Reitz R.D., Ogawa H., Payri R., et al., IJER editorial: the future of the internal combustion engine. International Journal of Engine Research, 2020, 21: 3–10.
[2]
Alagumalai A., Internal combustion engines: progress and prospects. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 38: 561–571.
[3]
Leach F., Kalghatgi G., Stone R., et al., The scope for improving the efficiency and environmental impact of internal combustion engines. Transportation Engineering, 2020, 1: 100005.
[4]
Guo C., Zuo Z., Feng H., et al., Advances in free-piston internal combustion engines: A comprehensive review. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 189: 116679.
[5]
Herold R., Wahl M., Regner G., et al., Thermodynamic benefits of opposed-piston two-stroke engines. SAE Technical Paper: 2011-01-2216, 2011.
DOI: 10.4271/2011-01-2216
[6]
Yuan C., Liu Y., Han C., et al., An investigation of mixture formation characteristics of a free-piston gasoline engine with direct-injection. Energy, 2019, 173: 626–636.
[7]
Zhang Q., Xu Z., Liu S., et al., Effects of injector spray angle on performance of an opposed-piston free-piston engine. Energies, 2020, 13: 3735.
[8]
Guo C., Song Y., Feng H., et al., Effect of fuel injection characteristics on the performance of a free-piston diesel engine linear generator: CFD simulation and experimental results. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 160: 302–312.
[9]
Zhang Z., Zhao C., Xie Z., et al., Study on the effect of the nozzle diameter and swirl ratio on the combustion process for an opposed-piston two-stroke diesel engine. Energy Procedia, 2014, 61: 542–546.
[10]
Zhang Z., Zhang P., Cross-impingement and combustion of sprays in high-pressure chamber and opposed-piston compression ignition engine. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 144: 137–146.
[11]
Yang J., Huang Z., Li G., et al., Analysis of influences of injection parameters on combustion process based on 2-stroke rod-less opposed piston diesel engine. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 236: 121637.
[12]
Mattarelli E., Cantore G., Rinaldini C.A., et al., Combustion system development of an opposed piston 2-stroke diesel engine. Energy Procedia, 2017, 126: 1003–1010.
[13]
Naik S., Johnson D., Koszewnik J., et al., Practical applications of opposed-piston engine technology to reduce fuel consumption and emissions. SAE Technical Paper: 2013-01-2754, 2013. DOI: 10.4271/2013-01-2754.
[14]
Liu S., Xu Z., Chen L., et al., Comparison of an opposed-piston free-piston engine using single and dual channel uniflow scavenging. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 201: 117813.
[15]
Ma F., Yang W., Xu J., et al., Experimental investigation of combustion characteristics on opposed piston two-stroke gasoline direct injection engine. Energies, 2021, 14: 2105.
[16]
Han Z., Reitz R., Turbulence modeling of internal combustion engines using RNG κ-ε models. Combustion Science and Technology, 1995, 106: 267–295.
[17]
Senecal P.K., Pomraning E., Richards K.J., et al., Multi-dimensional modeling of direct-injection diesel spray liquid length and flame lift-off length using CFD and parallel detailed chemistry. SAE Technical Paper: 2003-01-1043, 2003. DOI: 10.4271/2003-01-1043.
[18]
Reitz R.D., Beale J.C., Modeling spray atomization with the Kelvin-Helmholtz/Rayleigh-Taylor hybrid model. Atomization Spray, 1999, 9: 623–650.
[19]
Schmidt D.P., Rutland C.J., A new droplet collision algorithm. Journal of Computational Physics, 2000, 164: 62–80.
[20]
Som S., Development and validation of spray models for investigating diesel engine combustion and emissions. In: Mechanical Engineering, University of Illinois at Chicago, 2009.
[21]
Heywood John B., Automotive engines and fuels: a review of future options. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 1981, 7(3): 155–184.
[22]
Hiroyasu H., Kadota T., Models for combustion and formation of nitric oxide and soot in direct injection diesel engines. SAE Technical Paper: 760129, 1976.
DOI: 10.4271/760129.
[23]
Naber J., Siebers D., Effects of gas density and vaporization on penetration and dispersion of diesel sprays. SAE Technical Paper: 960034, 1996.
[24]
Zhang K., Liang Z., Wang J., et al., Diesel diffusion flame simulation using reduced n-heptane oxidation mechanism. Applied Energy, 2013, 105: 223–228.
[25]
Huang Z., Wang H., Luo K., et al., Direct numerical simulation of ammonia/n-heptane dual-fuel combustion under high pressure conditions. Fuel, 2024, 367: 131460.
[26]
Li Y., Li H., Guo H., et al., A numerical study on the chemical kinetics process during auto-ignition of n-heptane in a direct injection compression ignition engine. Applied Energy, 2018, 212: 909–918.
[27]
Liu L., Wu Y., Wang Y., et al., Comparison of the effect of diesel and hydrogen addition on ammonia combustion characteristics in a marine engine. SAE Technical Paper: 2023-32-0065, 2023.