KAN Xiaoxu
,
SUO Licheng
,
LEI Haodong
,
WU Wanyang
,
ZHONG Jingjun
. Shock Wave Spectrum Forming around the Compound Five-Hole Probe and its Influence on Pneumatic Parameters Acquisition during Subsonic to Supersonic Flow[J]. 热科学学报, 2024
, 33(6)
: 2019
-2031
.
DOI: 10.1007/s11630-024-2047-4
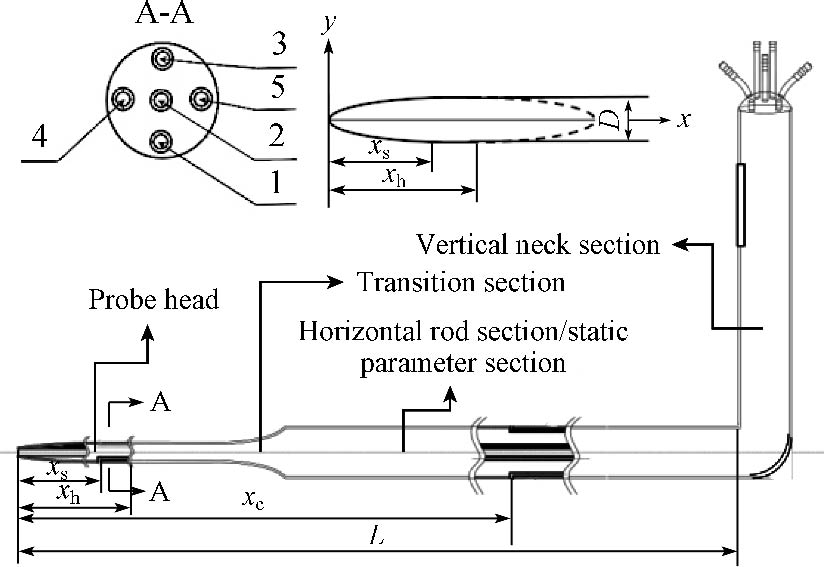
Supersonic wind tunnel experiment is one of the important measurements for developing advanced gas turbines, and supersonic multi-hole probes are sophisticated tools to measure pneumatic parameters in such experiments. However, shock waves form around the probe head in supersonic flow, which affect the accuracy of results. In this study, a supersonic five-hole probe is selected as the research object. Firstly, a compound five-hole pressure-temperature probe was designed and produced with 3D-printing technology. Then, the shock wave spectrum was numerically calculated by three methods, which were the Mach number, density gradient, and shock function; in contrast to the other two methods, the shock function could accurately identify the types and ranges of shock and expansion waves. The results show that a strong shock wave is formed at the front section of the probe head, and the shock wave generated around the pressure measuring tube affects the total pressure and Mach number of the flow field, which causes the increase of entropy. The intensity of the shock wave at the head of the pressure measuring tube is the largest, causing a decrease in the total pressure around the flow field. Afterwards, to reduce the calculation errors caused by neglecting the compressibility of gases and the entropy increase, a gas compression factor δs was introduced. It is proved that the error of the calculated pneumatic parameters is less than 5% and 10% in subsonic and supersonic condition, respectively, with the gas compression factor considered. The research results of this paper provide theoretical reference for the design and use of pneumatic probes during subsonic to supersonic flow.
[1] Valceres V.R.S., Wael K., Peter J.F., Performance optimization of gas turbine engine. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2005, 18(5): 575– 583.
[2] Shi Y.P., Wang J.L., Lu H.W., Sun X.Z., Wang Y., Investigation of nonlinear interpolation calculation method of five-hole probe under subsonic velocity. Chinese Journal of Turbomachinery, 2020, 62(04): 36– 45.
[3] Gao J., Wei M., Fu W.L., Zheng Q., Yue G.Q., Experimental and numerical investigations of trailing edge injection in a transonic turbine cascade. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 92: 258–268.
[4] Zhong J.J., Song Y.P., Lu W.C, Xu W.Y., Using of the non-nulling mode method of five-hole probe in the automatic survey system of wind tunnel. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 1997(03): 64–67.
[5] Ma H.W., He X., Shan X.M., Yao Z.R., A method for measuring 3-D unsteady flow at exits of a compressor rotor using combined probes. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2022, 37(10): 2253–2260.
[6] Passmann M., Wiesche S., Joos F., Numerical calibration of three-dimensional printed five-hole probes for the transonic flow regime. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2021, 143(5): 051501.
[7] Bryer D.W., Pankhurst R.C., Pressure-probe methods for determining wind speed and flow direction. The Aeronautical Joumal, 1971, 75: 660.
[8] Treaster A.L., Yocum A.M., The calibration and application of five-hole probes. ISA Transactions, 1979, 3(18): 23–24.
[9] Lin F., Zhang Y., Peng C.Y., The calibration technique of five-hole probe. Journal of Aerospace Power, 1990(03): 236–238, 285.
[10] Jian J., Qu J.Y., Zhao H.G., Study on development and calibration method for five-hole probe. Engineering & Test, 2014, 54: 59–63.
[11] Zhong J.J, Kan X.X., Yang L., A composite five-hole pressure-teperature probe. Shanghai, Patent No. CN211234909U, 2020-03-06.
[12] Carmen T., Supersonics: Principles and application. Science Press, 1959, pp: 41–45.
[13] Cheng K.M., The lateral shock wave family on the surface of a cone-cylinder in transonic flowfield. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 1991, (02): 256–259.
[14] Wang L., Huang G.F., Kan X.X., Zhong J.J., Numerical study on shock spectrum of supersonic five-hole probe with a large deflection angle. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2023, 44(04): 96–105.
[15] Ding T., Research of real-time measurement system and problems in compressible flow measurement for seven-hole probes. Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China, 2009.
[16] Zhang J.H., Investigation on aerodynamics of the supersonic flow past a cylinder. Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China, 2010.
[17] Zhang Q.D., Ma H.W., Yang Y., Zhong T.F., Effect of airfoil probe head on transonic turbine cascade flow field. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2022, 37(11): 2647–2658.
[18] Zhong J.J, Kan X.X., Wu W.Y., Yang L., A composite pressure-temperature probe and its flow velocity calculation method. Shanghai, Patent No. CN111551215A, 2020-06-28.
[19] Dong M., Ge N., Chen Y., Shock loss control methods for transonic turbine cascades. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2018, 33(05): 1226–1235.
[20] Zhang Y., Wu F., Feng X.D., Yin Y., Application and research of a supersonic five-hole probe with orthogonal ancillary holes. Aeroengine, 2018, 44(05): 65–72.
[21] Kan X.X., Huang G.F., Wu W.Y., Zhong J.J., Research on a method for calculating the high subsonic flow velocity measured by pneumatic probe. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2021, 42(07): 1700–1705.
[22] Goodyer M.J., A stagnation pressure probe for supersonic and subsonic flows. Aeronautical Quarterly, 1974, 25(2): 91–100.
[23] Hsieh T., Flow field study about a hemispherical cylinder in transonic and lowsupersonic Mach number range. 13th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, 1975, 1–11: 75–83.
[24] Zhong J.J, Huang G.F., Wu W.Y., Research on calculation method of aerodynamic parameters of supersonic probe based on gas compressibility actor. Journal of Thermal Science, 2022, 31(01): 111–119.



