

Influence Rules of Intensity and Circumferential Position of Induced Shock Wave on the Tip Flow Behaviors of a Transonic Rotor
网络出版日期: 2025-09-01
基金资助
This research work was sponsored by the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.52076124) and the Joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U2441278).
版权
Influence Rules of Intensity and Circumferential Position of Induced Shock Wave on the Tip Flow Behaviors of a Transonic Rotor
Online published: 2025-09-01
Supported by
This research work was sponsored by the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.52076124) and the Joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U2441278).
Copyright
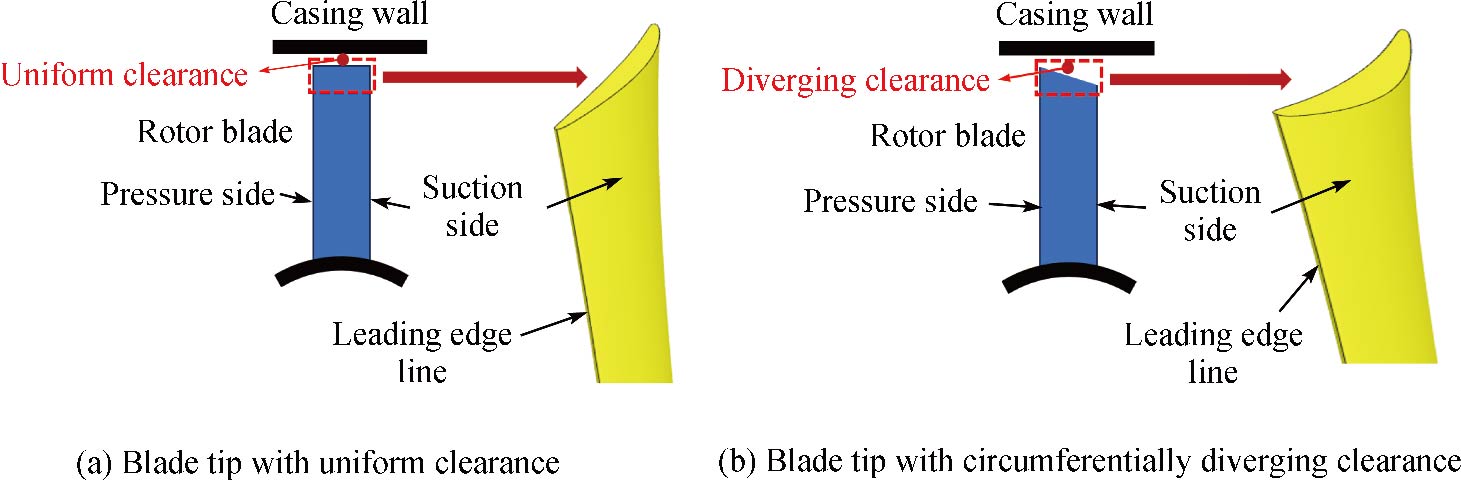
CUI Weiwei , ZHANG Long , ZHAO Qingjun , CHEN Xinyuan , CHANG Guozhang , WANG Cuiping . Influence Rules of Intensity and Circumferential Position of Induced Shock Wave on the Tip Flow Behaviors of a Transonic Rotor[J]. 热科学学报, 2025 , 34(5) : 1813 -1828 . DOI: 10.1007/s11630-025-2189-z

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |