TONG Shuiguang
,
CHEN Xin
,
TONG Zheming
,
YANG Qi
. Numerical Design and Optimization of Finned Tube Heat Exchanger with Curved Serration Based on Multi-Layered Neural Network and Tree-Structured Parzen Estimator Algorithm[J]. 热科学学报, 2025
, 34(4)
: 1417
-1430
.
DOI: 10.1007/s11630-025-2136-z
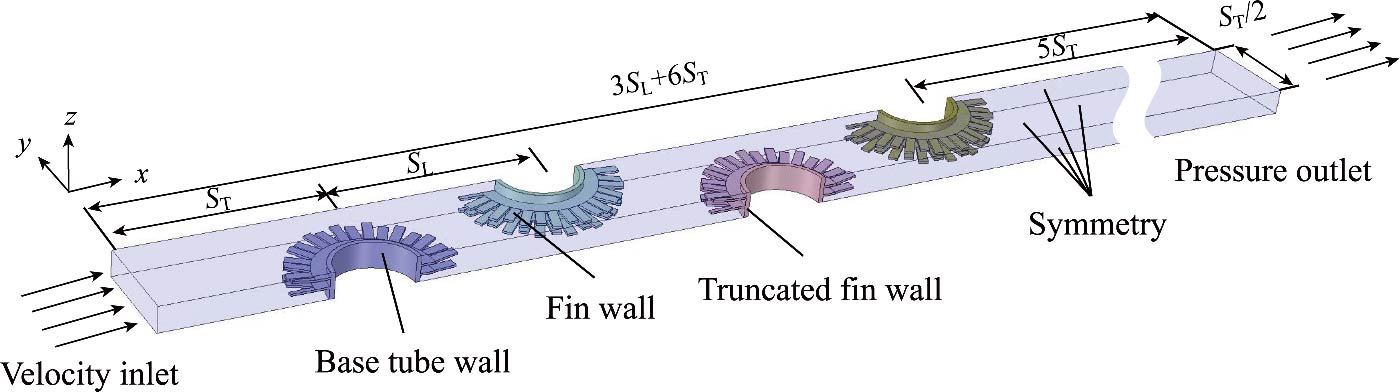
The Heat Recovery Steam Generators (HRSGs) are designed to recapture heat from gas turbine exhaust to generate electric power by a steam turbine. Finned tubes are critical heat transfer components of HRSG, whose design and optimization play an essential role in realizing effective energy utilization in power plants. In this study, an optimization method with multi-layered neural network (MNN) and tree-structured parzen estimator (TPE) is proposed for the finned tube heat exchanger with curved serration. This method has high fitting accuracy and global optimization efficiency, and is suitable for complex heat transfer design and optimization problems caused by novel irregular finned tubes. The developed thermal-fluid model is validated with existing experimental data, and a satisfactory agreement is found in terms of Nusselt number and Fanning friction factor. It is shown that increasing the curved serration angle is beneficial to destroy the thermal boundary layer and enhance turbulent kinetic energy. When the Reynolds number is between 5000 and 25 000, the heat transfer factor of finned tubes with a curved serration angle of 10° is 20% higher than that of flat serrated finned tubes on average. The optimized geometric parameters are obtained from the optimization approach, and the optimal solution has achieved excellent results in comprehensive performance. Compared with the baseline design, the optimized results show a 9% higher heat transfer factor, which is better than those based on commonly used optimization methods.
[1] Sadeghianjahromi A., Wang C.C., Heat transfer enhancement in fin-and-tube heat exchangers-a review on different mechanisms. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 137: 110470.
DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.110470.
[2] Mudhafar M.A., Pan H.Y., Optimization of condensation heat transfer on enhanced and integral fin tubes by functionalized-graphene layers. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 58(12): 2147–2160.
[3] Kiatpachai P., Pikulkajorn S., Wongwises S., Air-side performance of serrated welded spiral fin-and-tube heat exchangers. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 89: 724–732.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.04.095.
[4] Fan J., Ding W., Wu Z., He Y., Tao W., Zheng Y., Gao Y., Song J., A new performance evaluation method and its application in fin-tube surface design of small diameter tube. Frontiers in Energy, 2011, 5: 59–68.
DOI: 10.1007/s11708-010-0132-8.
[5] Zhou H., Liu D., Sheng Q., Hu M., Cheng Y., Cen K., Research on gas side performance of staggered fin-tube bundles with different serrated fin geometries. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 152: 119509.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119509.
[6] Lindqvist K., Næss E., A validated CFD model of plain and serrated fin-tube bundles. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 143: 72–79.
DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.07.060.
[7] Feng Z., Xin C., Zhou T., Zhang J., Fu T., Airside thermal-hydraulic and fouling performances of economizers with integrally-molded spiral finned tubes for residual heat recovery. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 211: 118365.
DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.118365.
[8] Lee M., Kang T., Kim Y., Air-side heat transfer characteristics of spiral-type circular fin-tube heat exchangers. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2010, 33(2): 313–320.
[9] Hofmann R., Walter H., Experimental and numerical investigation of the gas side heat transfer and pressure drop of finned tubes—Part II: numerical analysis. Journal of Thermal Science and Engineering Applications, 2012, 4(4): 041008.
[10] Zhang J., Hu X., Luo Y., Hui Z., Wang J., Yu T., Effects of rectangular wing vortex generators on the thermal-hydraulic performance of louvered fin and flat tube heat exchanger. Journal of Thermal Science, 2023, 32(2): 628–642.
[11] Kumar A., Joshi J.B., Nayak A.K., A comparison of thermal-hydraulic performance of various fin patterns using 3D CFD simulations. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 109: 336–356.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.01.102.
[12] Al Hilli A., Al-Ibadi M., Alfadhel A.M., Abdulshaheed S.H., Hadi A.H., Optimal path finding in stochastic quasi-dynamic environments using particle swarm optimization. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 186: 115706. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115706.
[13] Sanaye S., Hajabdollahi H., Thermal-economic multi-objective optimization of plate fin heat exchanger using genetic algorithm. Applied Energy, 2010, 87(6): 1893–1902.
[14] Tang S.Z., Wang F.L., He Y.L., Yu Y., Tong Z.X., Parametric optimization of H-type finned tube with longitudinal vortex generators by response surface model and genetic algorithm. Applied Energy, 2019, 239: 908–918.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.01.102.
[15] Ma X., Cao Q., Cui Z., Optimization design of the grate cooler based on the power flow method and genetic algorithms. Journal of Thermal Science, 2020, 29(6): 1617–1626.
[16] Hajabdollahi H., Shafiey Dehaj M., Masoumpour B., Ataeizadeh M., Optimal design analysis of a tubular heat exchanger network with extended surfaces using multi-objective constructal optimization. Frontiers in Energy, 2022, 16(5): 862–875.
[17] Tong Z., Yang Q., Tong S., Chen X., Two-stage thermal-hydraulic optimization for Pillow Plate Heat Exchanger with recirculation zone parameterization. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 215: 119033.
DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.119033.
[18] Tala J.S., Russeil S., Bougeard D., Harion J.L., Investigation of the flow characteristics in a multirow finned-tube heat exchanger model by means of PIV measurements. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2013, 50: 45–53.
DOI: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2013.05.003.
[19] Yakhot V., Orszag S.A., Renormalization group analysis of turbulence. I. Basic theory. Journal of Scientific Computing, 1986, 1(1): 3–51.
[20] Salim S.M., Cheah S. Wall y+ strategy for dealing with wall-bounded turbulent flows. Lecture Notes in Engineering and Computer Science, 2009, 2175(1): 1–6.
[21] Granda M., Trojan M., Taler D., CFD analysis of steam superheater operation in steady and transient state. Energy, 2020, 199: 117423.
DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117423.
[22] Ma Y., Yuan Y., Liu Y., Hu X., Huang Y., Experimental investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop in serrated finned tube banks with staggered layouts. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2012, 37: 314–323.
DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2011.11.037.



