Low-Reynolds-number effect is an important factor affecting the performance of compressors and other main components of high-altitude long-endurance unmanned aerial vehicles. To improve the flow condition and reduce flow loss under the condition of high altitude and low Reynolds number (Re), this paper proposes an optimization process based on a surrogate model, which combines the class-shape transformation method (CST), the Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) method, the light gradient-boosting machine algorithm (LightGBM), and a genetic algorithm (GA) to optimize a high-subsonic compressor profile. The surrogate model is verified to be accurate and can be used in the optimization process. The accuracy of the GA is higher than the other algorithms under common test functions. The optimization results are verified by numerical simulation, and the flow differences before and after optimization are compared, especially the flow within the boundary layer. By changing the blade shape, the optimization process adjusts the loading distribution to delay the transition of the optimized blade on the suction surface, which changes the turbulent reattachment in the laminar separation bubble (LSB) into laminar reattachment. Therefore, the mixing loss induced by the turbulent reattachment of the LSB and the wake loss of turbulent separation at the trailing edge are significantly reduced, and the performance of the compressor profile is finally improved. In addition, turbulent separation of the optimized profile is delayed reducing the range of the wake region on the suction surface. By this optimization process, the reduction of total pressure loss coefficient at Re of 2.5×105, 3.5×105, and 4.5×105 are 16.32%, 20.76%, and 22.16%, respectively.
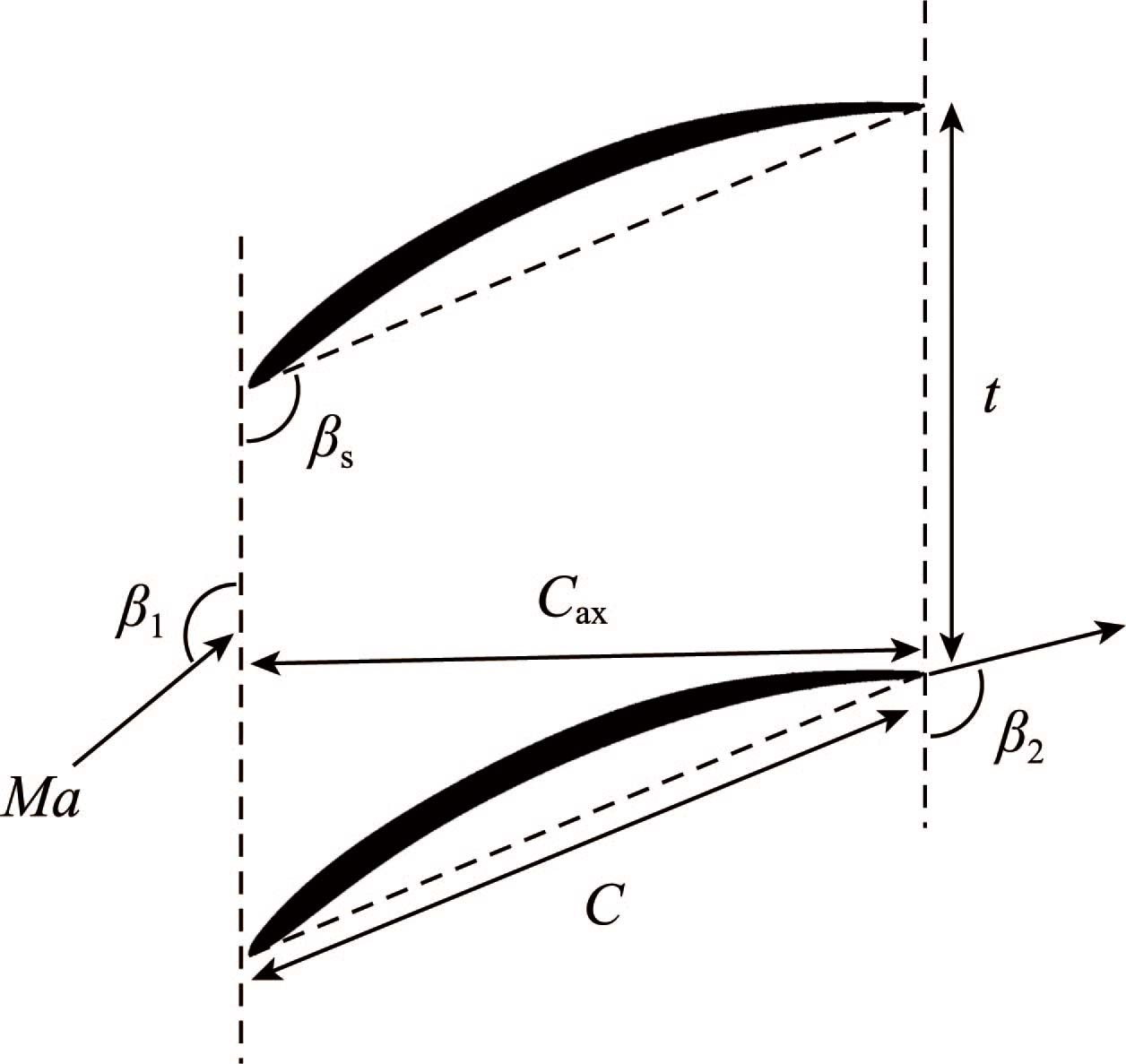
[1] Luo C., Song L., Li J., et al., A study on multidisciplinary optimization of an axial compressor blade based on evolutionary algorithms. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2012, 134(5): 054501.
[2] Girardeau J., Pailhes J., Sebastian P., et al., Turbine blade cooling system optimization. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2013, 135(6): 061020.
[3] Kenway G.K.W., Martins J.R.R.A., Multipoint aerodynamic shape optimization investigations of the common research model wing. AIAA Journal, 2016, 54(1): 113–128.
[4] Cheng J., Chen J., Xiang H., A surface parametric control and global optimization method for axial flow compressor blades. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019, 32(7): 1618–1634.
[5] Duan Y., Wu W., Zhang P., et al., Performance improvement of optimization solutions by POD-based data mining. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019, 32(4): 826–838.
[6] Xiang H., Chen J., Aerothermodynamics optimal design of a multistage axial compressor in a gas turbine using directly manipulated free-form deformation. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2021, 26: 101142.
[7] Forrester A.I.J., Keane A.J., Recent advances in surrogate-based optimization. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2009, 45(1): 50–79.
[8] Han Z.H., Zhang K.S., Song W.P., et al., Optimization of active flow control over an airfoil using a surrogate-management framework. Journal of Aircraft, 2010, 47(2): 603–612.
[9] Guo Z., Song L., Li J., et al., Research on meta-model based global design optimization and data mining methods. Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, 2015, Paper No: GT2015-42554, V02CT45A007.
[10] Liu Z., Liu X., Cai X., A new hybrid aerodynamic optimization framework based on differential evolution and invasive weed optimization. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2018, 31(7): 1437–1448.
[11] Adjei R.A., Wang W., Liu Y., Aerodynamic design optimization of an axial flow compressor stator using parameterized free-form deformation. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2019, 141(10): 101015.
[12] Adjei R.A., Fan C., Wang W., et al., Multidisciplinary design optimization for performance improvement of an axial flow fan using free-form deformation. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2020, 143(1): 011003.
[13] Li J., Ji L., Zhou L., Design optimization of a blended blade and endwall in a compressor cascade. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2020, 142(2): 021003.
[14] Wang Z., Qu F., Wang Y., et al., Research on the lean and swept optimization of a single stage axial compressor. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 15(1): 142–163.
[15] Du Q., Li Y., Yang L., et al., Performance prediction and design optimization of turbine blade profile with deep learning method. Energy, 2022, 254: 124351.
[16] Du Q., Yang L., Li L., et al., Aerodynamic design and optimization of blade end wall profile of turbomachinery based on series convolutional neural network. Energy, 2022, 244: 122617.
[17] Vincekovic L., John A., Qin N., et al., Exploring topology optimization for high pressure turbine blade tips. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2022, 144(7): 071013.
[18] Verstraete T., Amaral S., Van den Braembussche R., et al., Design and optimization of the internal cooling channels of a high pressure turbine blade—Part II: Optimization. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2010, 132(2): 021014.
[19] De Maesschalck C., Lavagnoli S., Paniagua G., Blade tip shape optimization for enhanced turbine aerothermal performance. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2013, 136(4): 041016.
[20] Dow E.A., Wang Q., The implications of tolerance optimization on compressor blade design. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2015, 137(10): 101008.
[21] Luo J., Chen Z., Zheng Y., A gradient-based method assisted by surrogate model for robust optimization of turbomachinery blades. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(10): 1–7.
[22] Sun J., Ottavy X., Liu Y., et al., Corner separation control by optimizing blade end slots in a linear compressor cascade. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 114: 106737.
[23] Luo J., Zhou C., Liu F., Multipoint design optimization of a transonic compressor blade by using an adjoint method. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2013, 136(5): 051005.
[24] He L., Wang D.X., Concurrent blade aerodynamic-aero-elastic design optimization using adjoint method. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2010, 133(1): 011021.
[25] Zhang Z.Q., Li P.J., Li Q.K., et al., Dynamic machine learning global optimization algorithm and its application to aerodynamics. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2023, 39(4): 524–539.
[26] Li L., Tan W., Zhang J., et al., Unsteady effects of wake on downstream rotor at low Reynolds numbers. Energies, 2022, 15(18): 6692.
[27] Kulfan B., Bussoletti J., “Fundamental” parameteric geometry representations for aircraft component shapes. 11th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, 2006, Paper No: AIAA 2006-6948.
[28] Stein M., Large sample properties of simulations using latin hypercube sampling. Technometrics, 1987, 29(2): 143–151.
[29] Walker G.J., Observations of separated laminar flow on axial compressor blading. Proceedings of the ASME 1975 International Gas Turbine Conference and Products Show, 1975, Paper No: 75-GT-63, V01BT02A001.



